BECA 831


Description
The BECA 831 profile is a standard floating seal or face seal composed of two metal parts made from 100Cr6 steel or Cast iron and two rubber Belleville seals.
Advantages
Wide temperature range, depending on the material chosen
Longer lifespan
Compact design
Straightforward development of the cylindrical housing, which requires a more precise fitting
Technical data
| Temperature | -60°C/+180°C |
|---|---|
| Pressure | 0.15 MPa in bearing steel in dynamic applications |
| Speed | 2.2 m/s in bearing steel |
| Medias | Oil lubrication |
Applications
Construction machinery
Screw conveyors for abrasive materials
Harvesting machinery
Materials
Metal friction rings
100Cr6 bearing steel
15CrMoNi cast iron
Durinit cast iron
Belleville seal
NBR 60 - 65 Shore A
HNBR 60 - 65 Shore A
FKM 60 - 65 Shore A
VMQ 60 - 65 Shore A
Dimensions
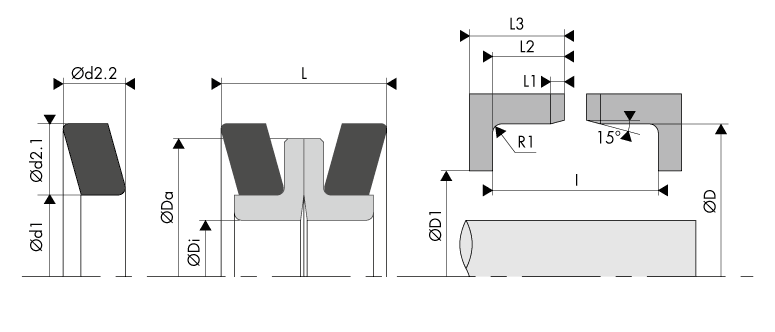
Installation dimensions
The diagram below sets out all of the elements that make up the BECA 831 floating seal as well as the housing into which it is inserted.
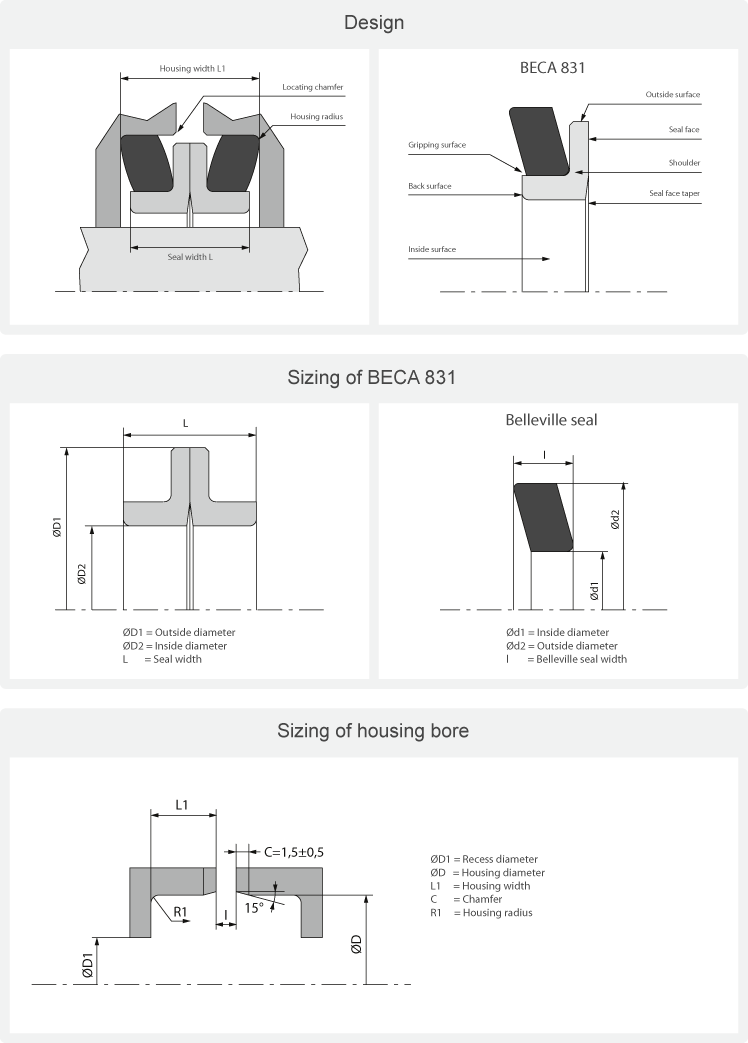
Materials
Metal parts
The metal parts can be made from two different materials.
15CrMoNi cast iron
The standard material used for the metal parts is 15CrMoNi cast iron with a hardness of 65 - 72 HRC and that has been developed to resist extreme conditions (environments that are abrasive, corrosive and have strong external demands). It can support a speed up to 3 m/s.
| Chemical composition in % | cast iron 15CrMoNi |
|---|---|
| C | 3.2 - 3.8 |
| Mn | 0.5 - 1.0 |
| Si | 1.0 - 2.0 |
| P | < 0.2 |
| S | < 0.2 |
| Cr | 14.0 - 16.0 |
| Ni | 0.4 - 0.6 |
| Mo | 0.8 - 1.2 |
| V | ≤ 0.2 |
Durinit cast iron
The Durinit material is a special Cast iron developed for applications that require permissible speeds of 10 m/s max. This special cast iron has a hardness of 58 - 65 HRC.
| Chemical composition in % | cast iron Durinit |
|---|---|
| C | 2.8 - 3.6 |
| Mn | 0.3 - 0.9 |
| Si | 1.5 - 2.0 |
| P | ≤ 0.3 |
| S | ≤ 0.1 |
| Cr | 2.5 - 3.0 |
| Ni | 3.5 - 4.0 |
| Mo | 0.3 - 0.5 |
| V | ≤ 0.4 |
100Cr6 bearing steel
The bearing steel type 100Cr6 with a hardness of 55 - 63 HRC is a more economical solution that can be used for the metal parts. This material can support a speed up to 2.2 m/s.
| Chemical composition in % | Standard steel 100Cr6 |
|---|---|
| C | 0.8 - 1.0 |
| Mn | 0.2 - 0.4 |
| Si | 0.2 - 0.3 |
| P | < 0.02 |
| S | < 0.02 |
| Cr | 0.8 - 1.5 |
| Ni | < 0.2 |
| Cu | < 0.2 |
| Mo | 0.02 - 0.08 |
Rubbers
NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber)
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is the general term for acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymer. The ACN content can vary between 18% and 50%. While the acrylonitrile content is important, the resistance to oil and fuel is more so. Conversely, the elasticity and compression set are not as good. The NBR has good mechanical properties and good wear resistance. However, its resistance to atmospheric agents and the ozone is relatively low.
| Chemical resistance | Aliphatic hydrocarbons (propane, butane, petroleum, diesel fuel) Mineral oils and greases Fire-resistant fluids (HFA, HFB and HFC) Diluted acids, low-temperature alkaline and saline solutions Water (up to +100°C max) |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Fuels with high aromatic content Aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene) Chlorinated hydrocarbons (trichlorethylene) Polar solvents (ketone, acetone, acetic acid, ethylene-ester) Strong acids Glycol-based brake fluids Atmospheric and ozone agents |
| Temperature range | -30°C / +100°C (short-term peak at +120°C) -40°C / +100°C with particular NBRs |
FKM (fluorinated rubber)
Depending on their structure and fluorine content, the chemical resistance and resistance to the cold in fluororubbers can vary. This FKM-based rubber is very often used for high-temperature hydraulics and pneumatics, for industrial valves, injection/fuel systems, motor seals and high-vacuum systems.
| Chemical resistance | Mineral oils and greases, ASTM n°1, IRM 902 and IRM 903 oils. Fire-resistant liquids (HFD) Silicone oils and greases Mineral and vegetable oils and greases Aliphatic hydrocarbons (propane, butane, petroleum) Aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene, toluene) Chlorinated hydrocarbons (trichlorethylene) Fuel (including high alcohol content) Atmospheric and ozone agents |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Glycol-based brake fluids Ammonia gas Organic acids with a low molecular weight (formic and acetic acids) |
| Temperature range | -20°C / +200°C (short-term peak at +230°C) -40°C / +200°C with particular FKMs |
HNBR (Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber)
This HNBR-based rubber is obtained through selective hydrogenation of the NBR's butadiene groups. It is commonly used for power-assisted steering and for air conditioning.
| Chemical resistance | Aliphatic hydrocarbons Mineral and vegetable oils and greases Fire-resistant fluids (HFA, HFB and HFC) Diluted acids, saline solutions and bases for operation at an average temperature Water and steam up to +150°C Atmospheric and ozone agents |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Chlorinated hydrocarbons Polar solvents (ketones, esters and ethers) Strong acids |
| Temperature range | -30°C / +150°C (short-term peak at +160°C) -40°C / +150°C with particular HNBRs |
VMQ (silicone rubber: methyl vinyl polysiloxane)
This FVMQ-based rubber is very often used in fuel systems.
| Chemical resistance | Animal and vegetable oils and greases Water for operation at an average temperature Diluted saline solutions Atmospheric and ozone agents |
|---|---|
| Compatibility issue | Superheated steam up to +120°C Chlorinated hydrocarbons with a low molecular weight (trichlorethylene) Aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene, toluene) |
| Temperature range | -60°C / +200°C (short-term peak at +230°C) |
The table below gives an overview of the physical, chemical and mechanical characteristics for each of the materials.
| Characteristics/Materials | FKM | HNBR | NBR | VMQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasion resistant | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Resistance to acids | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Chemical resistance | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Resistance to cold | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Dynamic properties | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Electrical properties | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Flame resistant | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| Heat resistant | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Sealing water | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Oil resistant | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Ozone resistant | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| Tearing resistant | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Traction resistant | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Water/vapour resistant | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Resistance to atmospheric agents | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
1. Excellent properties 2. Good properties 3. Average properties 4. Poor properties
Chemical compatibility
A "Chemical compatibility guide" catalogue can be downloaded from the Documentation section. You can also use our online "Chemical compatibility" tool free of charge.
These two tools give you the option of measuring the behaviour of our materials that come into contact with the majority of existing fluids. The data displayed is the result of rigorous testing of the ambient temperature and in consultation with previous publications. Test results are not fully representative due to the specific features of your application. The tests performed actually do not consider additives and impurities that may exist under the actual conditions of use, nor the potential elevation of temperatures. Other parameters can also alter the behaviour of our materials, such as the hardness, persistence, abrasion, etc. We therefore recommend performing your own tests to verify the compatibility of our materials according to your specific application. Our technical team can provide you with any additional information.
Technical data
Types of lubrication
For the system to operate correctly, it is necessary to lubricate the seal at the sealing gaps. We recommend using oil lubrication rather than grease lubrication.
- For an oil lubrication that is permanent and does not require upkeep, the oil level must be between the 2/3 of the inside diameter of the seal and the middle of the axis. We recommend using SAE 80 and SAE 90 gearbox oils for a better operation.
- Grease lubrication requires particular attention. It is avoided due to the hydrodynamic conditions of lubrication that cannot be met, which could lead to significant wear and therefore a premature deterioration of the seal. If grease lubrication is used, the grease must not be inserted between the friction surfaces of the seal.
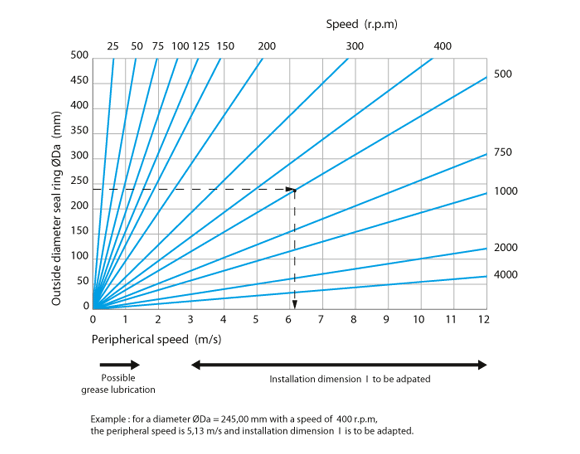
Limitations of use
The diagram below determines the linear speed (m/s), according to the outside diameter of the floating seal "D1" (mm) and its rotation speed (rpm).
Permissible pressure
The floating seals can be used for maximum pressures of 0.30 MPa for Cast iron and 0.15 MPa for 100Cr6 bearing steel.
Surface roughness
| Roughness | Contact surface area |
|---|---|
| Ra | ≤ 3.2 µm |
| Rz | ≤ 10.0 µm |
| Rmax | ≤ 16.0 µm |
|
831.004801
|
48,50 | 62,50 | 20,00 | 52,00 | 11,20 |
|
831.005601
|
56,00 | 76,00 | 21,00 | 60,50 | 10,50 |
|
831.006001
|
60,00 | 80,00 | 24,00 | 65,50 | 9,40 |
|
831.007301
|
73,50 | 93,00 | 20,00 | 80,00 | 10,20 |
|
831.007601
|
76,00 | 90,00 | 17,00 | 80,50 | 6,25 |
|
831.008801
|
88,00 | 104,00 | 18,00 | 92,00 | 9,50 |
|
831.009401
|
94,00 | 120,00 | 25,00 | 99,50 | 12,50 |
|
831.011501
|
115,00 | 141,00 | 28,00 | 120,50 | 14,70 |
|
831.013201
|
132,00 | 158,00 | 31,00 | 138,00 | 15,40 |
|
831.014201
|
142,50 | 161,00 | 24,00 | 147,00 | 11,70 |
|
831.014801
|
148,00 | 172,00 | 29,00 | 154,50 | 13,50 |
|
831.017701
|
177,00 | 197,00 | 22,00 | 179,00 | 11,00 |
|
831.020101
|
201,00 | 238,00 | 36,00 | 210,00 | 20,70 |
|
831.021301
|
213,50 | 238,00 | 27,40 | 219,00 | 16,00 |
|
831.023501
|
235,70 | 265,00 | 30,00 | 244,50 | 12,75 |
|
831.023901
|
239,00 | 264,00 | 34,00 | 244,50 | 15,80 |
|
831.028301
|
283,00 | 319,00 | 34,00 | 290,00 | 17,70 |
|
831.031901
|
319,00 | 353,00 | 36,20 | 326,00 | 17,50 |
|
831.035401
|
354,00 | 392,00 | 38,00 | 362,00 | 18,00 |
